Friday, July 8, 2011
Sunday, July 3, 2011
Introduction
PHYSICAL

The southern belt is almost plain land and the northern belt is rocky and mountainous where there are thousands of snow peaks. The mahabharat range that lies in between these two belts is the gently slopping land having river valleys and tars. This belts is gently slopping in the eastern parts and more steep in the western part.
The country is mainly drained by the three major river system namely koshi, gandaki and karnali from east to west respectively.
From the economic point of view, the terai is the extensive agricultural belt, the mid land is the fruit and gain crops growing area and the northern part is a very beautiful area suitable for touristic activities and livestock farming as well. In this way, diversity has been reflected in economic, social, cultural and other aspects of life. These make Nepal
POLITICAL
(Administrative division)
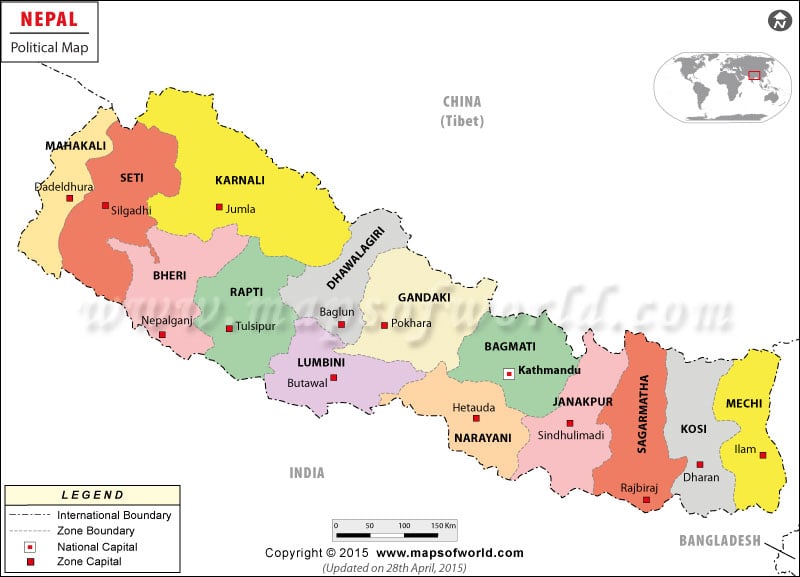
Each administrative division has its own headquarters. Dhankuta ,kathamandu ,Pokhara ,Birendranagar and Dipayal are the regional headquaters of the eastern, centeral,western,, Midwestern and farwestern development region respectively. Similarly, zones and districts also have their headquaters.Each VDC has its VDC office.
ECOLOGICAL DIVISION
The mountainous lies in the northernmost part. It covers about 35 percent land area where only about 7 percent cultivated land and about 8 percent population are found. The mountain lies above the altitude of 3000 metre where there is a large number of mangnificent snow-covered mountainous,including the highest peak (Mt.Everest 8848m)of the world . it coveres about 42 percent land area, 44.5 percent population and 37 percent cultivated land. It lies between 600m to 3000m altitude. This region comparise several attractive peaks, fertile valleys and river basins.The terai lies in the southern part of the country. It is elevated up to 600 meters from the sea level. It comparies 23 percent of the total land area, 49 percent population and 56 percent cultivated land . it has been formed out of alluvium brought and deposited by rivers. The land is fertile for agriculture where wide varieties of crops are grown.
PHYSIOGRAPHIC DIVISION
Physiographic refers to the study of surface land form characteristics, physiography of Nepal
Terai lies in the southern part . it is the plain land of altitude below 600 meter. The alluvial deposit forms it. The churiya lies just north of terai, formed with conglomerates. Then the middle mountain extends widely. It lies between 900 to 3000 meter altitudes . it has spurs, hill,river basins and valleys like kathmandu and pokhara . The high mountain also has steep and dissected land forms. The high himal is in the northernmost part where hundreds of snow peaks are found .
ELEVATION ZONES
The elevation of Nepal
RIVER NETWORK
These are three most important river system in Nepal Nepal
Beside these main rivers there are many other important rivers of second and third order. Some of these are Mechi, kankai, kamala, Bagamati , Tinau , Rapti , Babai, Mahakali, Ratu ,Lal –Bakaiya, Mohana, etc.
PEAK, PASS AND MOUNTAIN RIDGE
There are different mountain ranges in the Himal where the most hotable peaks are elevated. Some of the major mountain ranges are Mahalagur , Kumbhakarna,Singhalila, Rolwaling,Lantang-Lirung, Ganesh-larkehimal,Annapurna , Dhawalagiri,Api-saipal,etc. there are many passes in these mountain ranges.
Mount Everest (8848m),Choyou(8153m)Lhosthe(8501m)lies in the singhalila, Makalu(8475m)lies in the kumbhakarna , Machhapuchhare(6993m) and Annapurna (8091m) lie in Annapurna range and Dhaulagiri (8137m)lies in the Dhaulagiri range .
DISTRIBUTION OF MINERALS
The mountainous , hill and tarai regions have varied geological structure . Thus , various type s of minerals are found in Nepal
These minerals are of limited use for industrial purpose so far. Limestone and marble are explored to some extent for industries. But there is very limited survey , research and studies and it has still not been able to explore the condition of those minerals.
FOREST
Out of the total area in Nepal, forest covered only 29 percent area in 1994. Forest coverage is rapidly decreasing in our country. There was 38 percent forest in 1978/79 that was decreased to 35.9 percent in 1984. Not only has the coverage, the quality of the forest also been degrading. There is about 11 percent shrub area that was only about 5 percent in 1985/86.
Most of the forest of Nepal has been concentrated more of less along the East- West Highway. The forest of mild hill and mountain are massively degraded. There is 25.9 percent forest out of the total area in the EDR. Similarly, CDR, WDR, MWDR and FWDR have 33.5, 25.0, 28.2 and 35.2 percent forest area out of total land area of these development regions respectively. During the period of 1978 to 1994, the decreasing rate of forest was 1.7 percent in the national level.
PROTECTED AREAS
Nepal has given high priority to conserving and preserving the nature. There are eight national parks, five wildlife reserves and four conservation areNepal. The national parks, wildlife reserves and conservation areas have occupied 10144, 2398 and 17742 sq km area respectively. Altogether, the protected areas have covered 16.49percent (24284 sq km) area of the country.
Among the national parks, shey-phoksundo national parks are the largest (3555 aq km) and Rara National park is the smallest (106 sq km). The Royal chit wan National park is oldest national park of the country that is including in the world heritage site also. Similarly, out of the five wildlife reserves, Dolpatan Hunting reserve is the largest (1325 sq km) and shivapuri watershed wildlife reserve (144 sq km) is the smallest. Out of conservation areas, Annapurna conservation Area (7629 sq km) is the largest and Makalu Barun conservation Area (800 sq km) is the smallest in Nepal.
These protected areas of different ecological regions have conserved different valuable flora and fauna.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)








